Isometry
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- For the mechanical engineering and architecture usage, see isometric projection. For isometry in differential geometry, seeisometry (Riemannian geometry).
In mathematics, an isometry is a distance-preserving map between metric spaces. Geometric figures which can be related by an isometry are called congruent.
Isometries are often used in constructions where one space is embedded in another space. For instance, the completion of a metric space M involves an isometry from M into M’, a quotient set of the space of Cauchy sequences on M. The original space M is thus isometrically isomorphic to a subspace of a complete metric space, and it is usually identified with this subspace. Other embedding constructions show that every metric space is isometrically isomorphic to a closed subset of some normed vector space and that every complete metric space is isometrically isomorphic to a closed subset of some Banach space.
An isometric surjective linear operator on a Hilbert space is called a unitary operator.
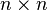

 is the
is the 

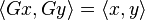

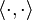 stands now for the standard
stands now for the standard  .
.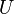 is an n by n matrix then the following are all equivalent conditions:
is an n by n matrix then the following are all equivalent conditions: